
The mass of the solute dissolved in 100 mL of the solution is known as mass by volume percentage.įor example, if 1 g of solute is dissolved in 100 mL of solution, the mass by volume percent of the solution is 1 percent (mass/volume). Mass percent = (mass of an element in 1 mole of compound/mass of 1 mole of a compound) x 100 The mass of a component is divided by the total mass of the mixture and multiplied by 100 percent to determine the mass percentage. The term " mass percentage (w/w)" refers to the concentration expressed as a percentage of one component in a solution by mass. This is referred to as weight/volume percent.įormula for calculating Volume Percentage Solute in a liquid form is relevant to the numerator in weight units and the denominator in volume units. In each scenario, the concentration is computed as a percentage of the solute's volume or weight in relation to the total volume or weight of the solution. Weight/volume percentage, volume/volume percentage, and weight/weight percentage are all examples of percent solutions. Read about: Difference between Mass and Weight To calculate % by mass, use the following formula:įormula of calculating percentage by mass To determine the percent by mass of a solute in a solution, we need two pieces of information: Multiplying the fraction of a solute in a solution by 100.The amount of solute in a 100-part solution.There are two aspects to be considered about percent by mass (or weight percent, as it is frequently called): It describes chemical concentration dissolved during a solvent (usually water) or compounds in a soil.
Parts per million (ppm) is what percentage parts a particular molecule or compound makes up within the million parts of the entire solution. The reciprocal quantity represents the dilution (volume) which can appear in Ostwald’s law of dilution.Determining Concentration of a Solution using Different MethodsĬoncentraton of a solution using different methods The molar concentration of the solute is sometimes abbreviated by putting square brackets around the chemical formula of the solute. One liter of a solution usually contains either slightly more or slightly less than 1 liter of solvent because when a substance dissolves in a solvent it causes a volume of liquid to increase or decrease.

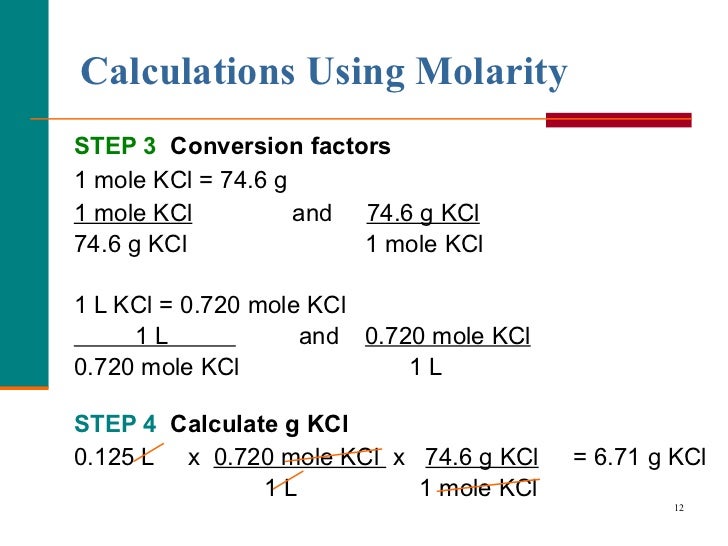
The volume, V in the definition, Ci = ni/V, refers to the volume of the solution, not the volume of the solvent. The molar concentration of a solute is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution ( not per liter of solvent). The molar concentration follows the same rules that the other units in the International System of Units. Specifically, it expresses the mole of a substance per liter of solution. Divide 0.1665 moles by 1.25 L to get the molar concentration, 0.1332 M. For example, the acetic acid in the above example is completely dissolved in 1.25 L of water. One mole of solute in one liter of water gives a concentration of 1 M. It can be used to convert between the mass or moles of solute and the volume of the solution. In chemistry, the molar concentration, Ci, is defined as the amount of a constituent, ni (usually measured in moles – hence the name) divided by the volume of the mixture, V: Ci = ni/V. It is the most convenient method of expressing the concentration of a solute in a solution. It measures the quantity of a substance per unit volume. It is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, which can be calculated using the following equation: Molarity = mol solute/L of solution. The concentration of a solution is basically a measurement of solute (B) with respect to the solution(S) or solvent(A).

It measures the concentration of a solution or mixture. Molar concentration, or molarity, or simply concentration, is a term in physical chemistry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
